How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You?

Tooth infections, often dismissed as mere annoyances, harbor the potential to escalate into life-threatening conditions if left untreated. These infections, originating in the tooth or its surrounding structures, can rapidly progress, leading to severe health complications and even death.
In this article, we delve into the symptoms, progression, and potential timeline for a tooth infection to become a serious threat to your health.
Table of Contents
Can a Tooth Abscess Kill You?
Yes, a tooth abscess can indeed pose a lethal threat if not promptly and properly treated.
An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms due to a bacterial infection in the tooth or surrounding gum tissue.
There are two main types: periapical abscess, which occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root, and periodontal abscess, which affects the gums next to the tooth root.
The danger of a tooth abscess lies not just in the localized infection but in its potential to spread. If the bacteria invade deeper tissues, they can reach the jaw, neck, and other parts of the body.
In extreme cases, the infection can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection that spreads throughout the body, causing organ failure and, in severe cases, death.
The infection can spread to the brain through the blood vessels, leading to abscesses or meningitis, which are both very serious conditions. Another risk is Ludwig’s Angina, an infection of the floor of the mouth, which can quickly swell and block the airways, making it difficult to breathe.
How long until a tooth infection kills you
It’s impossible to get a precise timeline for when a tooth infection becomes life-threatening. It can escalate from a localized issue to a severe systemic threat within days to weeks if not addressed. If the infection breaches into the bloodstream or migrates to other bodily areas, complications can become fatal.
When is a Tooth Infection an Emergency?
A tooth infection becomes an emergency when it exhibits signs of spreading or severe impact, such as intense, persistent pain; swelling in the face, cheek, or neck; fever; difficulty breathing or swallowing; and an overall feeling of malaise or illness.
If the infection leads to a sudden rush of foul-tasting fluid in your mouth, indicating abscess rupture, immediately seek a doctor. These symptoms suggest the infection could be spreading beyond the local area, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions like sepsis or airway obstruction.
When Does a Tooth Infection Become Life-Threatening?
A tooth infection becomes life-threatening when it spreads beyond the tooth to areas such as the jaw, neck, or brain, or when it leads to systemic issues like sepsis.
Warning signs include severe swelling, difficulty breathing or swallowing, high fever, and intense, unmanageable pain.
If the infection reaches the bloodstream, it can rapidly disseminate to other parts of the body, potentially causing organ failure or other critical conditions.
The Progression of a Tooth Infection
The progression of a tooth infection can unfold in several stages, evolving from a mild inconvenience to a severe health crisis if left untreated.
Here’s a general overview of how a tooth infection progresses:
1. Initial Bacterial Invasion
The journey of a tooth infection begins with bacteria penetrating the tooth’s protective enamel, often through a cavity, crack, or chip. These bacteria thrive on sugars and starches from food, producing acids that further erode tooth enamel, allowing the infection to reach the deeper layers of the tooth.
2. Decay and Damage to the Dentin
As the bacteria advance, they attack the dentin, the softer layer beneath the enamel. This progression can lead to sensitivity and pain as the dentin contains tiny tubes communicating with the nerve of the tooth. At this stage, professional dental intervention can prevent further damage and potentially save the tooth.
3. Infection of the Pulp
The pulp is the innermost part of the tooth, containing blood vessels and nerves. Once bacteria reach the pulp, the infection can cause it to swell, leading to pressure inside the hard confines of the tooth. This pressure can cause intense pain and, eventually, the death of the pulp tissue, creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
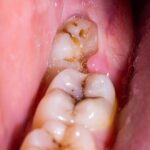
4. Abscess Formation
A dental abscess forms when the infection spreads beyond the confines of the tooth into the root and surrounding bone. This is a critical stage where the infection forms a pocket of pus, leading to severe pain, swelling, and the potential for the infection to spread into the bloodstream.
5. Systemic Spread
If not addressed, the bacteria from the abscess can enter the bloodstream, a condition known as bacteremia. From here, the infection can spread to distant parts of the body, potentially leading to serious conditions like sepsis, infection of the brain tissues, or other vital organs.
6. Critical Complications
In its most severe form, an untreated tooth infection can lead to life-threatening complications, including Ludwig’s angina, a type of cellulitis in the floor of the mouth that can obstruct breathing, or cavernous sinus thrombosis, a rare form of blood clot.
Sepsis, a body-wide response to infection, can lead to shock and organ failure, marking the most critical and potentially fatal stage of a tooth infection’s progression.
Can Antibiotics Cure a Tooth Infection?
Antibiotics can help manage a tooth infection by reducing the bacteria responsible for the infection, but they are not a cure-all. They are typically used in conjunction with other dental treatments, such as a root canal or tooth extraction, to fully eliminate the source of the infection.
Antibiotics are particularly useful when the infection has spread beyond the tooth or when there’s a risk of it spreading, helping to prevent further complications.
Still, they cannot restore the damaged tooth structure or remove the infected tissue, making dental intervention necessary to address the root cause of the infection. Read more: Can I Use Nitrofurantoin For Tooth Infection?
How do you know if a tooth infection is killing you?
If a tooth infection is becoming life-threatening, symptoms may include severe swelling in the face or neck, difficulty breathing or swallowing, high fever, rapid heart rate, confusion or disorientation, and intense, persistent pain. These signs indicate the infection may be spreading, potentially leading to severe systemic complications. Immediate medical attention is essential in such cases to prevent life-threatening outcomes.
How long can an infected tooth go untreated?
Leaving an infected tooth untreated is risky, and the time frame before serious complications arise can vary. While some infections may progress slowly over weeks or months, others can become life-threatening in a matter of days. The unpredictability of the infection’s spread shows how important it is to seek dental care promptly to prevent severe health issues.
What are the symptoms of a tooth infection spreading to the body?
Symptoms of a tooth infection spreading to the body include fever, swelling in the face or neck, severe pain, increased heart rate, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and fatigue. More severe signs include disorientation, rapid spread of swelling, and a general feeling of being unwell, indicating the infection may be affecting other parts of the body and possibly leading to systemic conditions like sepsis.
How do you know if tooth infection spread to brain?
If a tooth infection spreads to the brain, symptoms can include severe headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, confusion or altered mental state, seizures, and vision or speech changes. These signs indicate a serious, life-threatening condition, such as a brain abscess or meningitis, requiring immediate medical intervention.
Fact Checked
Our dedicated team rigorously evaluates every article and guide to ensure the information is factual, up-to-date, and free of bias.
Updated Regularly
We update our articles and reviews regularly to ensure you have access to the latest data in the dental industry.
The content on Dental3DU’s blog is intended for educational purposes only. This information should not be relied upon as professional medical counsel. Be sure to always consult with your dentist about the dangers and benefits of any medication, treatment or procedure.