Failed Gum Graft? Here Is What to Do
Facing the disappointment of a failed gum graft can be disheartening, especially when you’ve invested time, hope, and resources into improving your dental health and appearance.
Gum grafts, a common remedy for gum recession, involve transplanting tissue to the affected area, aiming to protect the teeth and restore the gum line. Despite high success rates, not all grafts take hold as expected.
We shed light on the complexities of gum graft failures, providing you with a deeper understanding of why grafts may fail, the signs to watch for, and the steps to take if you find yourself facing this setback.
Key Takeaways:
- Gum grafts treat receding gums, protecting teeth and improving aesthetics.
- Signs of failure include ongoing recession, pain, infection, loose graft, and bleeding.
- Success rates are high (76-98.4%), but failure can occur due to poor hygiene, smoking, infection, or other factors.
- If a graft fails, see your periodontist for next steps.
- To minimize risk, choose an experienced dentist, disclose medical history, quit smoking, and follow strict post-surgical care.
Table of Contents
What is a gum graft and its purpose?
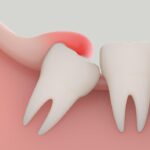
A gum graft, also known as a gingival graft, is a dental procedure used to treat gum recession, which occurs when the tissue surrounding the teeth pulls away from a tooth, exposing more of the tooth or its root.
This can lead to sensitivity, an increased risk of root decay, and aesthetic concerns.
The purpose of a gum graft is to:
- Protect teeth: By covering the exposed root, a gum graft can protect the tooth from decay and reduce sensitivity to hot and cold foods or drinks.
- Improve aesthetics: For patients concerned about the appearance of their receding gums, which can make teeth look longer than normal, a gum graft can help restore a more natural, youthful smile.
- Prevent further gum recession and bone loss: By reinforcing the affected area with new tissue, a gum graft can help prevent further recession and loss of bone around the teeth, contributing to better oral health.
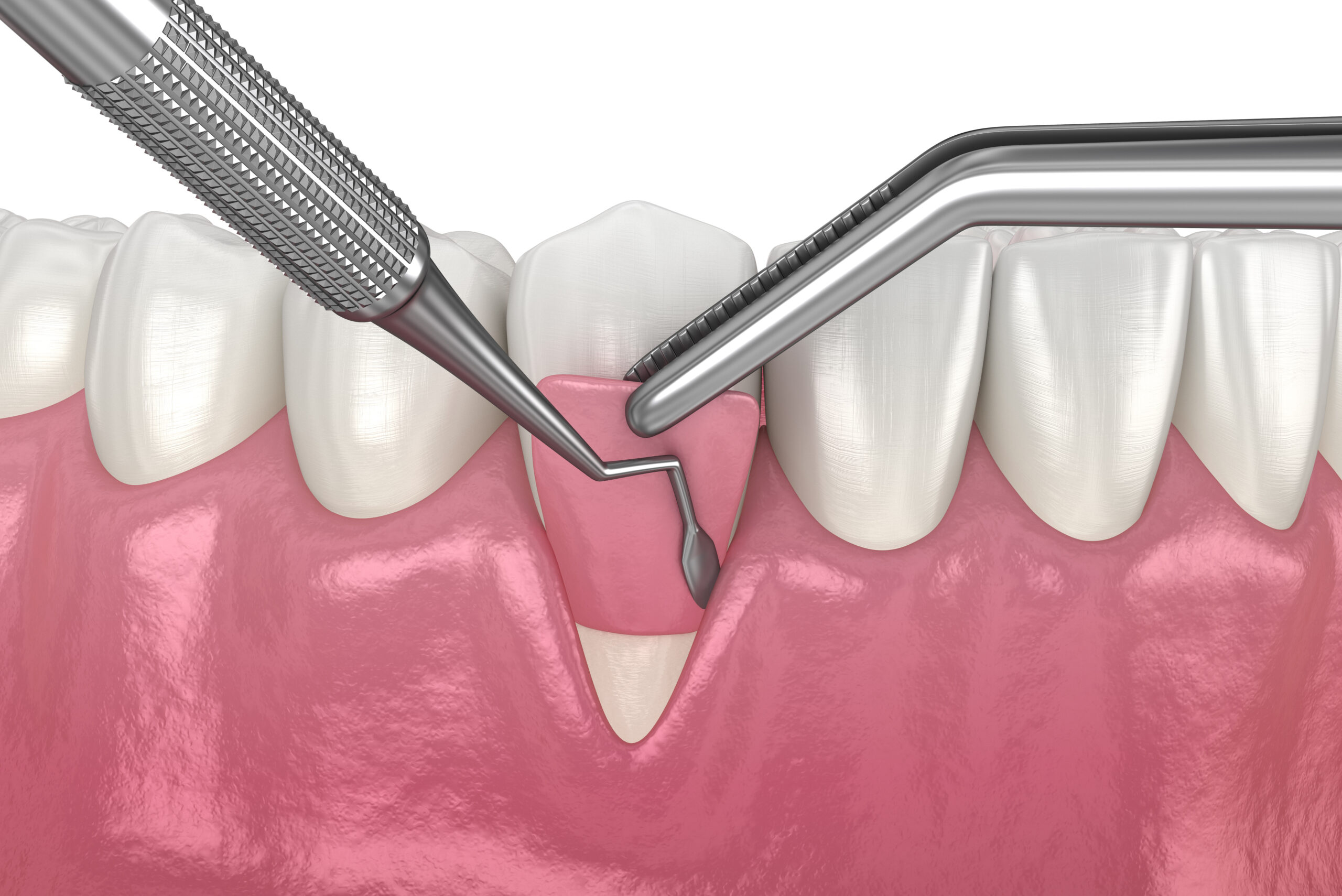
The procedure typically involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth, such as the palate, or using synthetic materials, and then grafting this tissue onto the area of gum recession.
How do you know if a gum graft has failed?
Key indicators of gum graft failure include:
- Persistent or increased recession: If the gum tissue continues to recede after the surgery, or if the recession worsens, the graft may have failed to integrate properly with the surrounding tissue.
- Severe pain or discomfort: While some pain and discomfort are normal after the procedure, severe or persistent pain beyond the expected healing period may indicate an issue with the graft.
- Infection signs: Symptoms such as excessive swelling, pus, an unpleasant taste, or fever can suggest an infection at the graft site, which can compromise the graft’s success.
- Loose or exposed graft material: If the graft material becomes loose or parts of it are exposed through the gum, this can indicate that the graft hasn’t successfully attached to the gum tissue.
- Bleeding: Some bleeding is normal immediately after surgery, but if it continues for days or starts again after initially stopping, it may be a sign of a problem.
- Lack of attachment: The grafted tissue should eventually integrate and attach firmly to the existing gum tissue. If it remains loose or detaches, the graft has not succeeded.
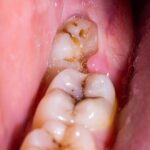
What does a failing graft look like?
A failing gum graft presents several visual and physical signs indicating that it is not healing properly or integrating with the surrounding tissues as intended. Based on our clinical experience, here are some of the most common signs of failing gum grafts:
- Color changes: The grafted area might appear excessively red, indicating inflammation, or white/grey, suggesting poor circulation or necrosis (tissue death) of the graft.
- No integration: Healthy gum tissue should start to integrate with the graft tissue. A lack of integration can appear as a clear demarcation between the graft and the existing gum, or the graft may look like it’s sitting on top of the gum without blending in.
- Excessive swelling or inflammation: While some swelling is normal after the procedure, prolonged or excessive swelling can indicate a problem, such as infection or rejection of the graft.
- Bleeding: A small amount of bleeding immediately after surgery is normal, but if the graft site continues to bleed for days afterward or resumes bleeding after initially stopping, it could signify a complication.
- Exposure of the graft material: In cases where the graft material becomes visible through the gums or seems to be coming loose, it indicates that the graft has not successfully attached to the underlying tissue.
What Are the Factors That Cause Gum Graft Failure?
Gum graft failure can occur due to several factors, often related to either the healing process, the condition of the oral environment, or the surgical technique.
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene can lead to infection at the graft site, which significantly impedes healing and can cause the graft to fail.
- Smoking: Smoking restricts blood flow and can delay healing, reducing the success rate of gum grafts. It also increases the risk of infection.
- Infection: Post-operative infections are a significant risk factor for graft failure. Keeping the surgical site clean and following post-operative care instructions carefully are crucial to prevent infections.
- Insufficient blood supply: The success of a graft heavily depends on a good blood supply to the grafted tissue. Areas with poor circulation or where the graft does not make good contact with the underlying tissue can lead to graft failure.
- Physical trauma: Biting down on the graft site, brushing too hard, or any physical trauma during the healing process can dislodge or damage the graft.
- Underlying health conditions: Conditions that affect healing, such as diabetes or autoimmune diseases, can increase the risk of graft failure.
- Inadequate graft size or type: Using graft material that is too small, too thin, or otherwise not suitable for the specific site can affect the outcome. The choice between autografts (tissue taken from the patient), allografts (tissue from a donor), or synthetic materials also plays a role in success rates.
- Patient non-compliance: Not following post-operative care instructions, such as avoiding certain foods, not taking prescribed medications, or failing to maintain proper oral hygiene, can lead to complications and graft failure.
- Technical errors: Errors in surgical technique, improper preparation of the recipient site, or inadequate fixation of the graft can compromise its success.
- Excessive movement: Too much movement in the area, either from the muscles around the mouth or from the tongue, can interfere with the healing process.
What percent of gum grafts fail?
Gum graft success rates are generally high, with studies reporting anywhere from 76% to 98.4% success rates. This means that failure rates are correspondingly low, at around 2-4%.
What to do after a failed gum graft?
While disappointing, a failed gum graft isn’t necessarily the end of the road. Here’s what to do next:
- See your periodontist: Don’t try to manage this on your own. Your periodontist can diagnose the cause of the failure and determine the best course of action.
- Follow their guidance: This may involve medication for infection or pain management.
- Consider retreatment: Sometimes, the procedure can be successfully redone, but there might be a waiting period of 3 months or so to allow proper healing.
- Discuss alternative treatments: If retreatment isn’t ideal, your dentist might suggest alternative approaches to address your gum recession.
- Minimize future risk: If you plan to undergo another gum graft procedure, discuss ways to minimize the risk of failure. This might involve improving oral hygiene habits or addressing any underlying causes of gum recession.
How to Minimize the Risk of Gum Graft Failure?
Minimizing the risk of gum graft failure involves several proactive steps before and after the procedure, focusing on both the preparation and the recovery phases.
Here’s how you can optimize the chances of a successful gum graft:
Before the Procedure
- Choose an experienced periodontist: Select a dental professional who specializes in gum surgeries and has a track record of successful grafts. Experience and expertise can significantly affect outcomes.
- Discuss your medical history: Inform your periodontist about your complete medical history, including any chronic conditions or medications that could affect healing or the surgery’s success.
- Quit smoking: If you smoke, try to quit well in advance of the surgery. Smoking can hinder healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Optimize overall health: Managing conditions like diabetes effectively can improve surgical outcomes, as controlled blood sugar levels support better healing.
After the Procedure
- Follow post-operative instructions carefully: Adhere strictly to your periodontist’s aftercare instructions, which may include guidelines on diet, oral hygiene, and activity restrictions.
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Keep your mouth clean to prevent infection. You may be advised to use a specific mouth rinse or a gentle brushing technique initially.
- Attend follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups allow your periodontist to monitor healing and catch any early signs of complications.
- Limit physical activity: Avoid strenuous activities that could increase blood pressure and cause bleeding at the graft site in the early healing stages.
- Eat soft foods: Stick to soft, nutritious foods that don’t require vigorous chewing, reducing stress on the graft site.
- Avoid directly brushing the graft site: Brush gently around the area and follow any specific cleaning instructions your dentist provides. Initially, you might need to avoid brushing the grafted area directly to protect it.
- Protect the graft: If you have a habit of grinding your teeth, consider using a night guard to protect the graft from excessive pressure.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help with overall health and the healing process, but avoid using a straw in the initial days following the surgery as the suction can disrupt the graft site.
- Report any concerns immediately: If you notice signs of infection, increased pain, or any other concerns, contact your periodontist right away.
How can I stimulate my gums to regenerate?
To stimulate gum regeneration, focus on maintaining excellent oral hygiene through regular brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily.
Use an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce bacteria. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids can support gum health. Avoid smoking and manage stress, as these can negatively affect gum health.
While these methods can help maintain healthy gums, actual regeneration of lost gum tissue may require professional dental treatments like scaling and root planing or regenerative procedures performed by a dentist or periodontist.
FAQ on Failed Gum Graft
When is a gum graft most likely to fail?
A gum graft is most likely to fail in the presence of poor oral hygiene, smoking, uncontrolled diabetes or other systemic conditions affecting healing, inadequate post-operative care, and failure to follow the dental professional’s instructions closely. Also,grafts may have higher failure rates if there is excessive movement of the graft site, infection, or if the patient engages in activities that disturb the site, such as brushing too hard, eating hard or crunchy foods too soon, or physical trauma.
What should a successful gum graft look like?
A successful gum graft should look healthy and well-integrated with the surrounding gum tissue, showing no signs of inflammation or recession. The color should closely match the rest of your gums, and there should be no excessive swelling, bleeding, or discomfort. Over time, the graft area becomes less distinguishable from the adjacent natural gum tissue, indicating that the graft has healed properly and is providing the necessary coverage and protection to the tooth’s root.
Can you ruin a gum graft?
Yes, a gum graft can be compromised or “ruined” by several factors, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, not following post-operative care instructions (such as eating hard or crunchy foods too soon), physical trauma to the graft site, or inadequate rest during the healing process. It’s crucial to closely follow your dentist’s or periodontist’s guidance to ensure the best outcome for your gum graft.
How long does it take for a gum graft to fully attach?
A gum graft typically takes about 4 to 6 weeks to fully attach and start blending with the surrounding tissue. Complete healing and stabilization of the graft can take up to 3 months or more, depending on individual health factors, the specific type of graft, and adherence to post-operative care instructions.
How fragile are gum grafts?
Gum grafts are relatively fragile in the initial days following the procedure, requiring careful management to ensure successful healing. During this period, you need to avoid direct trauma, harsh brushing, and eating hard or crunchy foods that could disturb the graft. Over time, as the graft heals and integrates with the surrounding tissue, it becomes less fragile and more resilient, although maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups remain important for its long-term success.
Fact Checked
Our dedicated team rigorously evaluates every article and guide to ensure the information is factual, up-to-date, and free of bias.
Updated Regularly
We update our articles and reviews regularly to ensure you have access to the latest data in the dental industry.
The content on Dental3DU’s blog is intended for educational purposes only. This information should not be relied upon as professional medical counsel. Be sure to always consult with your dentist about the dangers and benefits of any medication, treatment or procedure.