
Newsletter Subscribe
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter

Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
Ever wondered how to shrink gum pockets at home? Find out the best way to clean the gum pocket spaces and develop first-class oral hygiene at home.
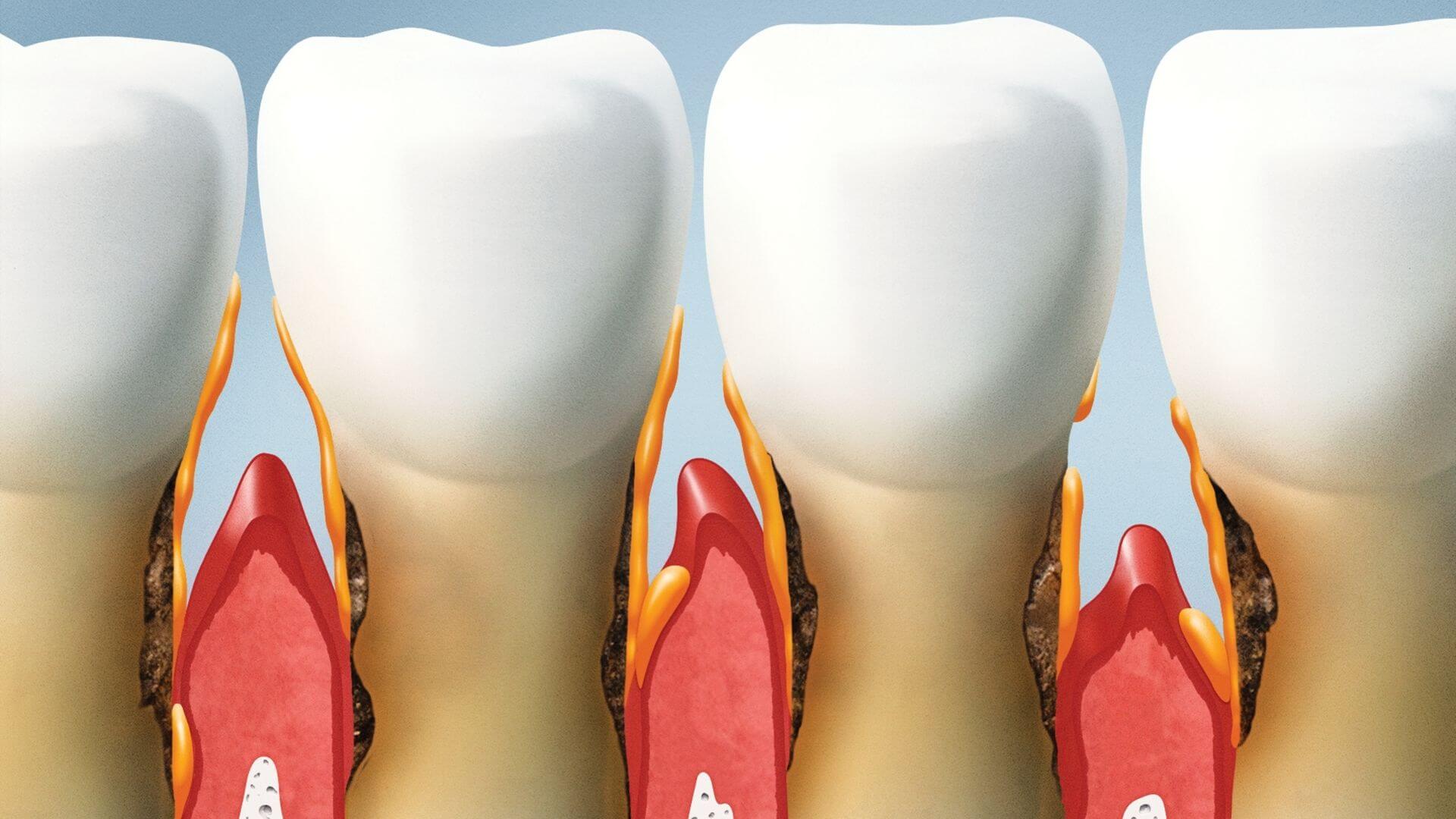
Gum pockets, also known as periodontal pockets, are spaces that can form around the teeth under the gum line when the gums pull away from the teeth.
These pockets can become breeding grounds for bacteria, leading to gum disease, tooth decay, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
While severe cases of gum disease require professional dental care, there are steps you can take at home to help shrink gum pockets and improve your oral health.
Gum pockets, also known as periodontal pockets, are spaces that form around the teeth under the gum line as a result of gum disease (periodontitis). These pockets can indicate the presence and severity of gum disease.
The most accurate way to know if you have gum pockets is through a professional dental examination. Dentists and periodontists use a special tool called a periodontal probe to measure the depth of the gum pockets around each tooth.
Healthy gums usually have pocket depths of 1 to 3 millimeters. Pockets deeper than 4 millimeters can indicate gum disease.
Gum pockets, or periodontal pockets, are caused by the progression of gum disease, which can be broken down into two main stages: gingivitis and periodontitis.
Here’s how these conditions lead to the formation of gum pockets:
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gum pockets, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes (such as those occurring during pregnancy), genetic susceptibility, certain medications that reduce saliva flow, and illnesses that affect the immune system.
Some individuals may be more prone to severe gum disease due to genetic factors. Aggressive periodontitis can occur in people who are otherwise healthy and can lead to rapid progression of gum pockets and bone destruction.
Preventing gum pockets involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Quitting smoking and managing other health conditions can also reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
If you already have gum pockets, treatment options include professional cleaning procedures like scaling and root planing, medications to control infection, and, in severe cases, surgery to restore supportive tissues.
Untreated gum pockets can lead to severe consequences, including progressive bone loss, tooth mobility, and eventual tooth loss due to the destruction of the supporting structures of the teeth.
As the pockets deepen, they harbor more bacteria, leading to further infection and inflammation. This chronic infection can also have systemic effects, potentially increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes complications, and respiratory issues.
Gum pockets are diagnosed through a combination of a dental examination and specific measurements taken by a dentist or periodontist (a gum disease specialist).
Here’s how the process typically works:
Based on the findings from these assessments, the dentist can determine the presence and severity of periodontal pockets and gum disease.
Treatment recommendations will depend on the severity of the disease and may range from improved home care and professional cleanings to more intensive treatments like scaling and root planing or surgery.
While professional treatment is essential for managing gum pockets and the underlying periodontal disease, there are several home care strategies you can employ to support your gum health and potentially reduce the depth of gum pockets.
Remember, these methods should complement, not replace, professional dental care. Here are some effective home care tips:
If you have gum pockets or signs of gum disease, consult with a dentist or periodontist for a personalized treatment plan.
The terms “gum pockets” and “periodontal pockets” are often used interchangeably to describe the same condition. Both refer to the spaces that form between the teeth and gums when the gum tissue pulls away or detaches from the teeth. This detachment is a result of the progression of gum disease, which is caused by the accumulation of plaque and its progression into tartar, leading to inflammation and infection of the gum tissue.
To clarify:
Both terms describe the same pathological condition associated with periodontal (gum) disease, where the depth of the space around the tooth increases beyond the healthy norm of 1 to 3 millimeters, indicating the presence of disease.
The use of either term generally points to the need for a comprehensive periodontal evaluation and, potentially, treatment to address the disease and prevent further damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth.
Gum pockets are spaces that form between the teeth and gums when the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth due to inflammation and infection. These pockets are a hallmark of periodontal disease, which progresses in stages from gingivitis to periodontitis.
The size of periodontal pockets is a key indicator of the severity of gum disease, and it is measured in millimeters using a periodontal probe.
Here’s a general guideline to understand the size and severity:
To reduce gum pocket size, maintain diligent oral hygiene by brushing twice daily, flossing, using an antiseptic mouthwash, and possibly incorporating interdental brushes or water flossers.
Reversing deep gum pockets at home is challenging; professional dental treatment is often required, though good oral hygiene can help prevent further deterioration.
Yes, salt water can help gum pockets by reducing inflammation and killing bacteria, but it should be used as a supplementary treatment rather than a primary solution.
Cleaning deep pockets in your gums involves professional dental cleaning methods like scaling and root planing, along with maintaining strict oral hygiene practices at home.
Hydrogen peroxide can help clean gum pockets by killing bacteria and reducing inflammation when used correctly, but it should be diluted and not used excessively to avoid irritation.
Reversing 7mm gum pockets typically requires professional dental treatments such as scaling and root planing, along with improved oral hygiene practices; complete reversal may not be possible, but treatment can prevent further damage.
While reversing 5mm gum pockets completely may be difficult, professional dental treatments combined with excellent oral hygiene can significantly improve the condition and prevent further progression.
Healing time for deep gum pockets varies; with professional treatment and diligent home care, some improvement can be seen in a few weeks, but complete healing may take months.
You cannot completely reverse 5mm gum pockets at home; professional dental care is necessary, though maintaining optimal oral hygiene can help improve the condition and prevent worsening.
Fact Checked
Our dedicated team rigorously evaluates every article and guide to ensure the information is factual, up-to-date, and free of bias.
Updated Regularly
We update our articles and reviews regularly to ensure you have access to the latest data in the dental industry.
The content on Dental3DU’s blog is intended for educational purposes only. This information should not be relied upon as professional medical counsel. Be sure to always consult with your dentist about the dangers and benefits of any medication, treatment or procedure.
Dental articles in your inbox. Subscribe