
Newsletter Subscribe
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter

Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
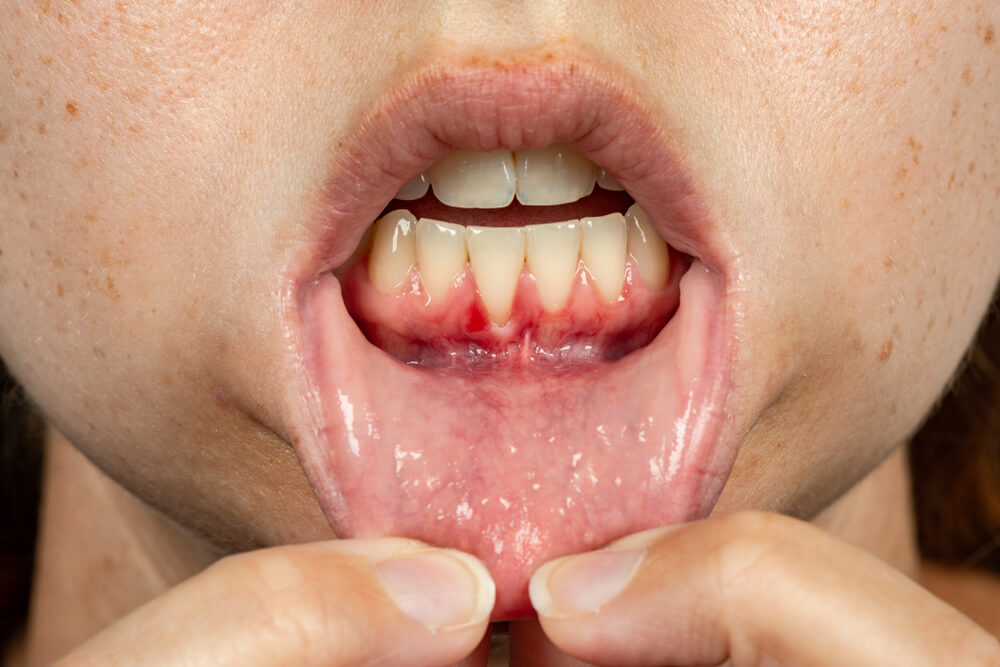
Learn about receding gums, including causes, prevention, and effective treatment options. Discover expert advice and tips to protect your oral health and stop gum recession in its tracks.
Receding gums occur when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. This condition can lead to sensitivity, increased risk of cavities on the tooth root, and aesthetic concerns.
Key Takeaways
Receding gums can be caused by several factors, often involving a combination of lifestyle habits and genetic predisposition. Common causes include:
Gum recession can affect people of all ages, but it’s more common in adults over the age of 65. This wider prevalence in older adults is often due to the cumulative effects of risk factors over time, such as poor oral hygiene habits, tobacco use, or untreated gum disease.
Younger adults and even teenagers are not immune, especially those with genetic predispositions to gum disease, those who practice aggressive tooth brushing, or those who have orthodontic issues that put additional stress on gums.
Gum recession is quite common and affects over 88% of people who are 65 and over.
Because gum recession can progress slowly and without pain in its early stages, many individuals may not realize they are affected until it becomes more pronounced. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and management.
Symptoms of receding gums can vary from mild to severe and often develop gradually. Here are some of the key symptoms to look out for:
The treatment for receding gums often involves surgical procedures, especially in cases where non-surgical methods such as deep cleaning or medication cannot address the issue effectively.
The types of surgery used to treat receding gums include:
This is the most common surgical treatment for gum recession. It involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth (such as the palate) or using a donor material and grafting it onto the areas where the gums have receded.
This procedure helps to cover exposed roots, reduce sensitivity, and improve the appearance of your smile.
When the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed due to gum disease, we usually recommend a regenerative procedure.
This involves folding back the gum tissue, removing the bacteria, and then using regenerative materials like membranes, bone grafts, or tissue-stimulating proteins to encourage your body’s natural ability to regenerate bone and tissue in the area.
In cases where the spaces between your teeth and gums (pockets) are too deep to clean effectively, this procedure might be used. The gum tissue is folded back, bacteria are removed, and the tissue is then secured in place over the tooth root, reducing the depth of the pocket.
I’ve had patients looking for ways to shrink gum pockets at home, but always consult with a dentist for such procedures. In most cases, you’ll do more harm than good.
This is a minimally invasive option for treating gum recession. Instead of grafting, a small hole is made in the gum tissue, through which special tools are used to gently loosen the gum tissue and slide it over the areas of the teeth with receding gums.
The choice of procedure depends on the severity of the gum recession, the health of the patient, and specific needs or preferences. A consultation with a periodontist or a dental specialist is necessary to determine the most appropriate treatment option.
Gum recession is often caused by periodontal disease, aggressive brushing, poor oral hygiene, genetic predisposition, tobacco use, and hormonal changes. Grinding or clenching your teeth can also contribute.
Gum tissue does not regenerate like other tissue types, so receded gums cannot grow back. However, treatments like gum grafts can cover exposed roots and reduce further recession.
Prevent receding gums by maintaining good oral hygiene, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, avoiding aggressive brushing, and getting regular dental check-ups to detect early signs of gum disease.
Symptoms include increased tooth sensitivity, visibly longer teeth, and exposed tooth roots. You might also notice a notch near the gum line.
Treatments range from non-surgical options like scaling and root planing to surgical interventions such as gum grafts and the pinhole surgical technique, depending on severity.
While the thought of gum grafting might seem daunting, it’s generally well-tolerated with local anesthesia. Post-operative discomfort is usually manageable with over-the-counter or prescribed pain relief.
Yes, if left untreated, receding gums can lead to tooth loss. Recession often exposes tooth roots, making them more susceptible to decay and periodontal disease.
The typical cost for gum graft surgery varies between $600 and $1,200 for each tooth. Should gum contouring be added to enhance the aesthetic appeal of the gums, this procedure could increase the overall cost by several hundred dollars.
While maintaining good oral hygiene is paramount, some natural remedies like oil pulling, green tea, and vitamin C can support gum health. Don’t forget, they’re not substitutes for professional treatment.
Smoking is a major risk factor for periodontal disease, which can lead to gum recession. It impairs blood flow to the gums, hindering healing and making smokers more prone to gum disease.
Fact Checked
Our dedicated team rigorously evaluates every article and guide to ensure the information is factual, up-to-date, and free of bias.
Updated Regularly
We update our articles and reviews regularly to ensure you have access to the latest data in the dental industry.
The content on Dental3DU’s blog is intended for educational purposes only. This information should not be relied upon as professional medical counsel. Be sure to always consult with your dentist about the dangers and benefits of any medication, treatment or procedure.
Dental articles in your inbox. Subscribe