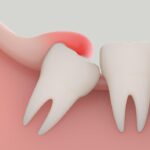
Mandibular tori removal
Mandibular tori, those bony growths that can appear along the inner surface of the lower jaw, often go unnoticed until they start to interfere with daily life.
Whether it’s making dental procedures more complicated, causing discomfort, or affecting the fit of dentures, the decision to remove these benign but bothersome protrusions can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of mandibular tori removal, offering essential insights into when removal is advised, what the surgical process entails, and how to navigate the recovery phase effectively.
We also provide practical advice on managing any potential complications, ensuring you’re fully informed and prepared for a smoother dental experience.
If you’re contemplating surgery or simply curious about your options, this article is your go-to resource for understanding mandibular tori removal.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of Mandibular Tori overgrowth
Mandibular tori (torus mandibularis, if it’s one) are bony growths located on the inner side of the lower jaw, below and near the tongue. They are generally benign and vary in size.
Overgrowth of mandibular tori can lead to several symptoms or issues, including:
- Discomfort or pain: As the tori grow, they may cause discomfort or pain, especially if they come into contact with food or when speaking.
- Difficulty eating: Large tori can interfere with chewing, making it difficult to eat certain foods. They may also cause discomfort when eating hard or crunchy foods.
- Speech difficulties: In some cases, the overgrowth can affect speech, making it difficult to pronounce certain sounds or words clearly.
- Oral hygiene challenges: Larger tori can make it challenging to maintain good oral hygiene, as they create hard-to-reach areas that may accumulate food particles and plaque.
- Mucosal ulceration: The overlying mucosa (the membrane covering the tori) can become ulcerated if repeatedly traumatized by food or during dental procedures.
- Interference with dental procedures: Mandibular tori can interfere with the fitting of dentures, dental impressions, or other dental appliances and procedures.
- Aesthetic concerns: In some cases, if the tori are particularly large, they might be visible and cause aesthetic concerns.
Why do you need mandibular tori removal?
Mandibular tori removal is not always necessary, as these bony growths are generally benign. However, there are specific circumstances under which removal might be considered or required:
Discomfort or pain
If the tori cause significant discomfort or pain during eating, speaking, or other activities, removal might be recommended to alleviate these symptoms.
Interference with oral functions
Large tori can interfere with chewing, speaking, and the overall comfort of the mouth. If they significantly affect oral functions, removal can help restore normal function and comfort.
Oral Hygiene Difficulties
If the presence of tori makes it difficult to maintain good oral hygiene, leading to recurrent oral health issues like plaque buildup, tooth decay, or periodontal disease, removal might be considered to facilitate better oral care.
Dental Prosthesis Fitting
Mandibular tori can interfere with the fitting and comfort of dentures or other dental appliances. If tori prevent proper fitting or cause discomfort with dentures, removal might be necessary for a better fit and function.
Complications
Although rare, if the tori are subject to frequent trauma leading to ulceration or infection of the overlying mucosa, removal might be recommended to prevent further complications.
Aesthetic Concerns
In some cases, if the tori are large and cause significant aesthetic concerns for the patient, removal might be considered for cosmetic reasons.
Benefits of mandibular tori removal
Types of mandibular tori removal
Mandibular tori removal can be performed using different surgical techniques, depending on the size and location of the tori, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s preference and expertise.
Here are the primary types or techniques of mandibular tori removal:
Traditional Surgical Removal
This method involves making an incision over the tori, exposing the bone, and then using surgical instruments to remove the bony growth. The area is smoothed, and the incision is sutured closed.
Suitable for tori of various sizes, especially larger ones that require significant bone removal.
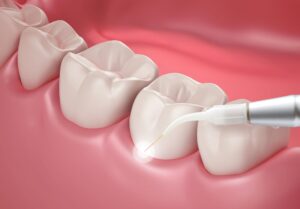
Laser Surgery
Laser surgery uses a focused beam of light to cut tissue and remove the tori. It can seal blood vessels, reducing bleeding during the procedure.
Often used for smaller tori or in situations where precision and minimal invasiveness are desired. It’s noted for reduced postoperative discomfort and faster healing times.
How is tori removal surgery performed?
Tori removal surgery, also known as torus mandibularis removal or excision, is a procedure performed to remove bony growths in the mouth, specifically on the inner side of the lower jaw (mandibular tori) or the roof of the mouth (palatal tori).
The surgery aims to alleviate discomfort, improve oral function, or prepare the mouth for dental prostheses.
Here’s a general overview of how the surgery is performed:
Preoperative Assessment
- Initial Consultation: The surgeon evaluates the patient’s oral health, the size and location of the tori, and discusses the reasons for removal, potential benefits, and risks associated with the surgery.
- Imaging: X-rays or CT scans may be taken to assess the size and density of the tori and to plan the surgical approach.
- Medical History: A review of the patient’s medical history to identify any conditions that might affect the surgery or anesthesia.
Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area around the tori. In some cases, sedation or general anesthesia may be used, especially if the patient is anxious or if the tori are large.
Surgical Procedure
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the gum tissue overlying the tori.
- Removal: Using surgical instruments, the surgeon carefully removes the bony growth. This may involve chiseling or drilling to section the torus into smaller pieces for easier removal.
- Smoothing: After removal, the surgeon smooths the underlying bone to prevent sharp edges that could irritate the tongue and gums.
- Closure: The gum tissue is then sutured back into place over the surgical site.
Mandibular tori removal recovery
Recovery from mandibular tori removal varies among individuals, depending on the extent of the surgery, the individual’s overall health, and the specific technique used for removal.
Here are some general guidelines and expectations for the recovery period:
Immediate Postoperative Period
- Bleeding: Some bleeding is normal within the first 24 hours. Patients are often advised to bite gently on gauze pads to control it.
- Swelling: Swelling is common and can peak 2-3 days after surgery. Applying ice packs to the face in the first 48 hours can help minimize swelling.
- Pain Management: Pain can be managed with prescribed medications or over-the-counter pain relievers, as recommended by the surgeon.
- Diet: A soft or liquid diet is usually recommended for the first few days to avoid irritating the surgical site. Gradually reintroduce solid foods as comfort permits.
Oral Hygiene
- Mouth Rinsing: Patients may be advised to start gently rinsing with warm salt water or a prescribed oral rinse 24 hours after surgery to aid healing and keep the area clean.
- Brushing: Careful brushing around the surgical site can usually resume after a few days, avoiding direct contact with the healing gums.
Activity
- Rest: Patients should rest and avoid strenuous activities for the first few days to reduce bleeding, swelling, and discomfort.
- Elevation: Keeping the head elevated when lying down can help reduce swelling.
Follow-up Care
- Suture Removal: If non-resorbable sutures are used, they typically need to be removed 1-2 weeks post-surgery.
- Check-ups: Follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Healing Time
- Initial Healing: The gum tissue usually starts to heal within a week, with significant improvement over the next 2-3 weeks.
- Complete Bone Healing: The underlying bone may take several months to fully remodel and heal.
Potential Complications
While complications are rare, it’s important to be aware of signs that may indicate a problem:
- Persistent Bleeding: A little oozing is normal, but heavy bleeding that doesn’t stop with pressure may need attention.
- Excessive Swelling or Bruising: Some swelling and bruising are normal, but if it worsens after 2-3 days, consult your surgeon.
- Severe Pain: Pain should gradually decrease after surgery. Persistent or worsening pain may indicate infection or other issues.
- Infection: Signs include persistent swelling, redness, warmth, or pus discharge from the surgical site, and fever.
What is the cost of oral tori removal, and does dental insurance cover it?
The cost of oral tori removal can vary widely depending on several factors, including the geographic location of the dental practice or oral surgeon’s office, the complexity of the case, the specific technique used for the removal, the anesthesia type, and whether additional treatments are required in conjunction with the tori removal.
Cost of Oral Tori Removal
The cost for oral tori removal can range from $600 to several thousand dollars. The wide range reflects differences in surgical approaches (e.g., traditional surgery vs. laser surgery), the number of tori being removed, and the need for any specialized care.
Factors Influencing Cost
- Location: Costs can be higher in urban areas or regions with a higher cost of living.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: Surgeons with extensive experience or specializations may charge more.
- Facility Fees: If the procedure is performed in a hospital or surgical center, there may be additional facility fees.
- Anesthesia: The type of anesthesia (local vs. general) can affect the overall cost. General anesthesia or IV sedation, which requires an anesthesiologist or nurse anesthetist, usually adds to the cost.
- Additional Procedures: If other dental work is done simultaneously, such as dental implant placement or bone grafting, the total cost will be higher.
Insurance Coverage
Many dental insurance plans consider tori removal to be a covered procedure, especially if it is deemed medically necessary rather than purely cosmetic. For example, if the tori interfere with oral functions, cause pain, or prevent the proper fitting of dentures, insurance may cover part or all of the procedure.
In some cases, if there’s a medical reason for the removal, medical insurance might cover the procedure. This is less common and depends on the specifics of the insurance policy.
It’s often necessary to get pre-authorization from the insurance company before the procedure. The dental office or surgeon’s office may assist with this process, providing necessary documentation to demonstrate the medical necessity of the procedure.
FIND OUT MORE: How To Get Dental Insurance without a Job
Recommendations
- Get an Estimate: Before proceeding with surgery, obtain a detailed estimate from the oral surgeon or dentist. This should include all associated costs, such as anesthesia, facility fees, and any postoperative care.
- Check Insurance Coverage: Contact your dental and medical insurance providers to understand your coverage, including any deductibles, copays, or coinsurance you may be responsible for.
- Consider Payment Plans: Some dental offices offer payment plans or financing options to help manage the cost of the procedure.
FAQ on Mandibular tori removal
How painful is mandibular tori removal?
Mandibular tori removal pain varies individually but is generally manageable with local anesthesia during the procedure, minimizing discomfort. Postoperative pain can be expected but is typically controlled with prescribed pain relievers or over-the-counter medications. Most patients report the pain as mild to moderate, subsiding significantly within the first few days after surgery. Proper postoperative care can further alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
How long does it take to recover from Tori surgery?
Recovery from tori surgery typically takes a few weeks for initial healing, with complete bone healing possibly taking several months. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days, although dietary restrictions and oral hygiene precautions are advised to support healing.
Should I get my Tori removed?
Deciding to remove tori depends on whether they cause discomfort, interfere with oral functions, or affect dental appliance fitting. If tori lead to pain, difficulty eating, or oral hygiene challenges, removal might be considered. Consult with a dental professional to evaluate your specific situation and discuss potential benefits and risks.
How do I stop my mandibular tori from growing?
There’s no proven method to stop the growth of mandibular tori, as their development is influenced by factors like genetics, jaw structure, and possibly stress on the jawbones. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups can help monitor their size and address any issues early.
If I have my torus removed, will it grow back?
After torus removal, it’s uncommon but possible for the torus to regrow, especially if underlying factors like genetic predisposition or specific jaw stressors persist. Regular dental check-ups can help monitor any changes and address potential regrowth early.
Fact Checked
Our dedicated team rigorously evaluates every article and guide to ensure the information is factual, up-to-date, and free of bias.
Updated Regularly
We update our articles and reviews regularly to ensure you have access to the latest data in the dental industry.
The content on Dental3DU’s blog is intended for educational purposes only. This information should not be relied upon as professional medical counsel. Be sure to always consult with your dentist about the dangers and benefits of any medication, treatment or procedure.