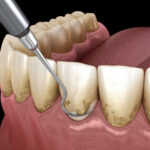
What causes a Bump on the Roof of Mouth?
A bump on the roof of your mouth can be caused by various conditions, ranging from minor issues that may resolve on their own to more serious conditions that require medical attention.
Here are the common causes of a bump on the roof of your mouth and treatment advice.
Table of Contents
The Most Common Causes for a Bump on the Roof of Your Mouth
Canker Sores
Small, shallow ulcers that can make eating and talking uncomfortable. They’re not contagious and usually go away on their own within 1-2 weeks. The exact cause is unknown, but factors like stress, minor mouth injuries, and acidic foods can trigger them.
Symptoms: Painful ulcers, tingling or burning sensation before the sores appear.
Treatment: Over-the-counter topical treatments, mouth rinses, and pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort. Avoiding spicy or acidic foods can also reduce irritation.
Mucoceles
Mucous cysts that form when a salivary gland is blocked or injured. These cysts are filled with clear fluid and can occur on the lips, floor of the mouth, or the roof of the mouth.
Symptoms: Soft, round cysts that are movable and painless.
Treatment: Many mucoceles resolve on their own, but persistent or large cysts may require surgical removal by a dentist or oral surgeon.
Torus Palatinus
A benign, bony growth in the middle of the roof of the mouth. It’s a genetic condition that’s more common in women and doesn’t usually require treatment unless it interferes with speech, eating, or fitting of dental appliances.
Symptoms: Hard, bony mass in the center of the roof of the mouth.
Treatment: No treatment is necessary unless it causes discomfort or interferes with oral functions, in which case surgical removal is an option.
Cold Sores (Herpes Simplex Virus)
Contagious viral infections causing painful blisters. They’re caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and can recur throughout a person’s life.
Symptoms: Painful blisters or ulcers on the lips, around the mouth, and sometimes on the roof of the mouth; may be preceded by tingling or burning.
Treatment: Antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks. Over-the-counter creams and oral pain relievers can also alleviate symptoms.
Oral Thrush
A fungal infection caused by Candida yeast. It’s more common in infants, elderly people, and those with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms: White, creamy lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, and roof of the mouth, which can be painful and bleed when scraped.
Treatment: Antifungal medications are used to treat oral thrush. Maintaining good oral hygiene and controlling underlying conditions can help prevent recurrences.
Squamous Papilloma
Benign tumors caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear anywhere in the mouth and are usually painless.
Symptoms: Small, wart-like growths that can be pink, white, or the same color as the surrounding tissue.
Treatment: Surgical removal is typically recommended to eliminate the growth and for biopsy purposes to rule out malignancy.
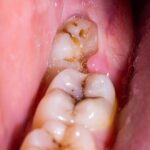
Nasopalatine duct cyst
The Nasopalatine Duct Cyst (NPDC), also known as an incisive canal cyst, is the most common non-odontogenic cyst of the oral cavity. It originates from the nasopalatine duct, the embryological communication between the nasal cavity and the oral cavity.
This cyst is typically located in the midline of the anterior maxilla, just behind the upper front teeth (incisors). While it can occur at any age, it is most frequently diagnosed in adults between the ages of 40 and 60.
Many nasopalatine duct cysts are asymptomatic and are often discovered incidentally during routine dental radiographs. When symptoms do occur, they may include: swelling in the area of the cyst, pain or discomfort, especially if the cyst becomes infected, displacement of adjacent teeth if the cyst grows large enough, occasionally, drainage of fluid into the mouth
Nicotine Stomatitis
A condition seen in smokers due to the heat from smoking, not the nicotine itself. It causes the salivary glands on the roof of the mouth to become inflamed and the mouth’s lining to thicken.
Symptoms: Whitish appearance of the mouth’s roof with raised red dots, which are inflamed salivary glands.
Treatment: The primary treatment is to quit smoking. The condition usually reverses after smoking cessation.
Burning Mouth Syndrome
A condition causing a burning sensation in the mouth without any visible signs. Its cause is often unknown, but it can be associated with other health conditions.
Symptoms: Burning sensation in the mouth, changes in taste, dry mouth.
Treatment: Treatment focuses on underlying causes, if known, and symptom relief through medications, saliva replacements, and dietary changes.
Trauma
Injury to the mouth from biting, burns, or irritation from sharp or hot foods can cause bumps or swelling.
Symptoms: Pain, swelling, or a bump in the area of injury.
Treatment: Most minor injuries heal on their own. Avoiding spicy or acidic foods and using over-the-counter pain relievers can help.
Allergic Reactions
Reactions to certain foods, medications, or materials (like dental appliances) can cause swelling and bumps in the mouth.
Symptoms: Swelling, itching, bumps in the mouth, possibly accompanied by other allergic reaction symptoms.
Treatment: Identifying and avoiding the allergen is key. Antihistamines can help manage symptoms.
Dental Appliances
Poorly fitting dentures, braces, or other dental appliances can irritate the mouth’s roof, leading to bumps or ulcers.
Symptoms: Pain, discomfort, or sores where the appliance irritates the mouth.
Treatment: Adjusting the offending appliance is necessary to relieve irritation. Dental wax can help cushion braces.
Sinus Infections
Infections or inflammation of the sinuses can cause pressure and bumps on the roof of the mouth due to the close proximity of the sinuses.
Symptoms: Pain or pressure in the face, headache, nasal congestion, and sometimes a bump on the roof of the mouth.
Treatment: Treatment may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, decongestants, and saline nasal sprays. Drinking plenty of fluids and using a humidifier can also help relieve symptoms.
Epstein pearls
Epstein pearls are small, white or yellowish cysts found in the mouths of newborns, typically along the gums or the roof of the mouth. They are harmless and result from the entrapment of epithelial cells during mouth development.
Epstein pearls affect up to 80% of newborns and usually disappear on their own within a few weeks of birth, requiring no treatment. These benign cysts are not painful or dangerous and are considered a normal part of newborn development.
Hyperdontia
Hyperdontia is a dental condition characterized by the development of extra teeth beyond the normal set. These supernumerary teeth can appear in any area of the dental arch and may affect both primary (baby) and permanent teeth.
Hyperdontia can lead to dental issues such as crowding, misalignment, or delayed eruption of adjacent teeth. The exact cause is unknown, but it may be linked to genetic factors or certain syndromes.
Treatment often involves the removal of the extra teeth, especially if they cause discomfort or affect dental health, followed by orthodontic treatment to correct any alignment issues.
Ectopic teeth
Ectopic teeth are teeth that erupt or develop in an abnormal position outside their usual location. This condition can affect any tooth but is most commonly seen with the maxillary canines and molars.
Ectopic eruption can lead to complications such as crowding, displacement of adjacent teeth, or impaction. The exact cause is not clear but may involve genetic factors, overcrowding, or developmental issues.
Treatment depends on the severity and may include monitoring, orthodontic intervention to guide the tooth into its proper position, or extraction if the tooth poses a risk to adjacent teeth or oral health.
Strep throat
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, or group A streptococcus, affecting the throat and tonsils. Common in children and adolescents, it presents with symptoms such as sore throat, fever, red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white patches or streaks of pus, painful swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes. Diagnosis is confirmed through a rapid strep test or throat culture.
Treatment typically involves antibiotics to reduce the duration of symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce infectiousness. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage symptoms. Without treatment, strep throat can lead to serious complications like rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation.
Oral cancer
Oral cancer refers to cancers of the mouth and throat, part of a larger group known as head and neck cancers. It often starts in the flat cells that line these areas (squamous cells). Risk factors include tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, HPV infection, and excessive sun exposure to the lips.
Symptoms may include sores that don’t heal, lumps, pain, difficulty swallowing, and voice changes.
Early detection can significantly improve the prognosis. Treatment options vary based on the cancer’s stage and location and may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Regular dental check-ups can help in early detection.
FAQ on What Causes a Bump on the Roof of Mouth
What does a bump in the roof of your mouth mean?
A bump in the roof of your mouth can indicate various conditions, ranging from harmless cysts like mucoceles or Epstein pearls to more serious issues such as oral cancer or infections. It could also result from trauma, allergic reactions, or dental problems. While many bumps are benign and may resolve on their own, persistent or painful bumps should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Should I be worried about a lump in my mouth?
A lump in your mouth can often be benign, but it’s important to monitor it, especially if it persists for more than two weeks, grows, or is accompanied by symptoms like pain, difficulty swallowing, or color changes. These could be signs of conditions ranging from infections to oral cancer.
Can sinus infection cause bump on roof of mouth?
Yes, a sinus infection can cause a bump on the roof of your mouth. This occurs due to the close proximity of the sinuses to the oral cavity, leading to swelling and inflammation that can manifest as a bump or lump. Such symptoms are typically accompanied by other signs of sinus infection, including nasal congestion, facial pain, and pressure. The bump should reduce as the sinus infection is treated and resolves.
What causes a palatal torus?
A palatal torus is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is a benign bony growth on the roof of the mouth (palate) and tends to be more common in certain populations and families, suggesting a hereditary component. Other contributing factors may include dietary habits, particularly diets high in hard or tough foods that require more chewing, which could stimulate bone growth. However, the exact cause of palatal torus development is not fully understood.
How do I get rid of a bump on the roof of my mouth?
The treatment for a bump on the roof of your mouth depends on its cause. Many bumps, such as mucoceles or minor injuries, heal on their own without treatment. However, for persistent or painful bumps, or those caused by infections, treatment may include:
– Good oral hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing can prevent infection and promote healing.
– Rinsing with salt water: Helps reduce inflammation and soothe discomfort.
– Avoiding irritants: Such as hot, spicy, or acidic foods that can aggravate the bump.
– Medication: Antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungal treatments for oral thrush, or antiviral drugs for viral infections.
– Surgical removal: In cases of cysts, tumors, or other growths that do not resolve on their own.
Should I be worried about torus palatinus?
Torus palatinus is generally not a cause for concern. It is a benign, bony growth on the roof of the mouth that typically does not require treatment unless it causes discomfort, interferes with speech, eating, or the fit of dental appliances. If you experience any of these issues, consult a dentist or oral surgeon for advice. Regular dental check-ups can help monitor the torus for any changes that might necessitate intervention.
How long does a bump on roof of mouth last?
The duration a bump on the roof of the mouth lasts can vary widely depending on its cause. Minor injuries or irritations might heal within a few days to a week, while bumps caused by infections or canker sores could take 1-2 weeks to resolve. Conditions like mucoceles or cysts might persist until treated. If a bump does not improve within two weeks, or if it grows or becomes painful, see your dentist.
What does torus palatinus look like?
Torus palatinus appears as a hard, bony lump or growth in the middle of the roof of the mouth (palate). It can vary in size and shape, ranging from small and flat to large and nodular. The overlying mucosa (mouth lining) is usually normal in appearance, covering the bony growth. Torus palatinus is benign and typically does not change much once fully developed, although its size can vary between individuals.
Does torus palatinus go away?
Just like mandibular tori, torus palatinus does not typically go away on its own. It is a permanent bony growth on the roof of the mouth that remains once it has developed. The size and prominence of the torus can vary among individuals, but it generally remains stable over time without treatment. Surgical removal is possible but usually only recommended if it causes significant discomfort, interferes with speech, eating, or the fit of dental appliances. For most people, torus palatinus is a benign condition that does not require intervention.
Fact Checked
Our dedicated team rigorously evaluates every article and guide to ensure the information is factual, up-to-date, and free of bias.
Updated Regularly
We update our articles and reviews regularly to ensure you have access to the latest data in the dental industry.
The content on Dental3DU’s blog is intended for educational purposes only. This information should not be relied upon as professional medical counsel. Be sure to always consult with your dentist about the dangers and benefits of any medication, treatment or procedure.