Mandibular Tori Vitamin Deficiency
Can Mandibular Tori Be Influenced by Vitamin Deficiency?
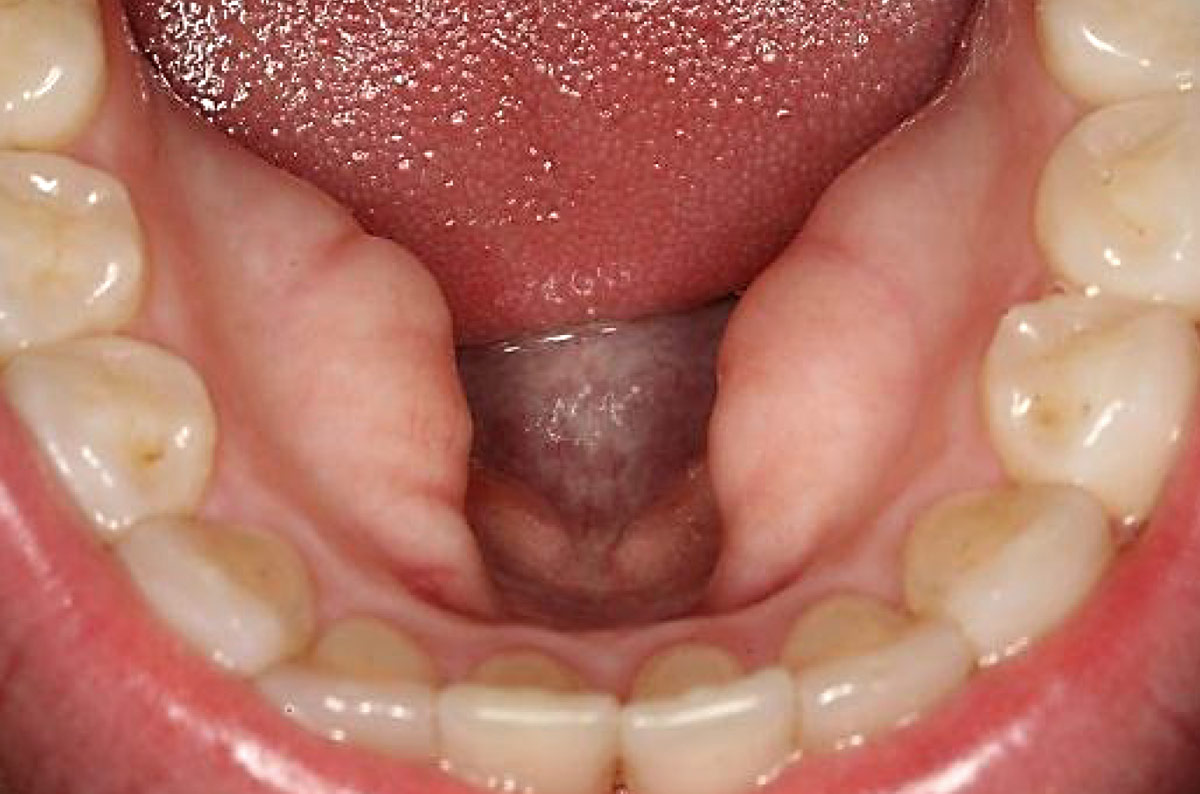
Mandibular tori are bony growths that develop along the inner surface of the lower jaw (mandible). These growths are generally benign and are thought to be influenced by several factors, including genetic predisposition and mechanical stressors such as teeth grinding.
Although there isn’t a direct and established link between mandibular tori and vitamin deficiencies, overall nutrition can impact bone health.
Key Takeaways
- Mandibular tori aren’t directly caused by vitamin deficiency. Their growth is primarily linked to genetics and jaw stress.
- Vitamin D is crucial for bone health. Deficiency can negatively impact the jawbone, potentially making existing tori more noticeable or problematic.
- Other vitamins matter too. Vitamin C, vitamin K, and B vitamins all play roles in oral health. Deficiencies can lead to gum disease, sores, and other complications.
- Research is ongoing. Studies suggest a correlation between low vitamin D and decreased bone density, including in the jaw, but more investigation is needed to form a definitive link specific to mandibular tori.
Table of Contents
The effects of vitamin D deficiency on mandibular bone structure
The study aimed to evaluate the effects of vitamin D deficiency on the mandibular bone structure by fractal analysis and panoramic morphometric indices. READ STUDY.
Quick Summary
- Vitamin D and Immunity: Vitamin D deficiency is associated with various diseases, including COVID-19, due to its significant role in both innate and adaptive immune responses.
- Bone Health: Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining bone strength and mineral balance. Deficiency can lead to conditions like rickets, osteomalacia, and increased bone fractures. It’s involved in the process where calcium transitions from bone to blood, influenced by hormones such as PTH and 1,25(OH)2D3.
- Dental Radiography Studies: Several studies have utilized dental radiography to assess bone quality. Techniques like Fractal Dimension (FD) analysis have proven effective in identifying low bone mineral density through panoramic and CBCT radiographs. These studies also explored the diagnostic potential of different radiographic techniques and indices (e.g., MCI, MCW, PMI) in detecting osteoporotic changes in craniofacial bones.
- Specific Findings:
- FD analysis indicates that patients with conditions like chronic renal failure, thalassemia major, and sickle cell anemia have lower bone mineral densities compared to controls.
- Medications like bisphosphonates, antiepileptic drugs, and SSRIs have been shown to affect bone mineral density as observed in FD values.
- Studies also noted that vitamin D deficiency specifically leads to decreased bone mineral density and increases alveolar porosity.
- Periodontal Disease and Vitamin D: Lower serum levels of Vitamin D were significantly associated with periodontitis, suggesting that Vitamin D deficiency might exacerbate alveolar bone loss and periodontal tissue degeneration.
- Dental Treatment and Vitamin D: There’s an observed correlation between low serum Vitamin D levels and higher rates of dental implant failures. This underscores the potential benefits of Vitamin D supplementation in improving outcomes for dental treatments.
- Limitations and Future Research: The study highlighted limitations such as the retrospective nature and insufficient sample size for certain Vitamin D levels. Future studies are recommended to include larger populations and possibly the maxilla to provide a more comprehensive understanding of Vitamin D’s effects on oral bone health.
The Importance of Vitamins for Bone Health
Vitamins and minerals essential for bone health include:
- Calcium: Fundamental for bone formation and maintenance. Deficiency can lead to weakened bone structure.
- Vitamin D: Crucial for calcium absorption in the bones. Vitamin D deficiency can affect bone density and lead to bone disorders.
- Vitamin K: Plays a role in bone metabolism and in the synthesis of proteins necessary for bone health.
- Magnesium: Important for bone formation as it helps with the activation of vitamin D.
What are the main effects on vitamin deficiency for oral health?
Vitamin deficiencies can significantly impact oral health in various ways. Here are some key vitamins and the effects of their deficiencies on oral health:
- Vitamin D:
- Deficiency in Vitamin D can lead to impaired bone mineralization, which affects the health and strength of both the jawbone and teeth. This can increase the risk of periodontal disease and tooth loss.
- Lack of Vitamin D may also increase susceptibility to infections, including periodontal disease.
- Vitamin C:
- Vitamin C is crucial for the maintenance of healthy gums and the prevention of gingivitis (gum inflammation). It is essential for collagen synthesis, which helps maintain the integrity of the periodontal ligament and other supportive structures of the teeth.
- A deficiency in Vitamin C can lead to scurvy, which manifests in oral health as swollen, bleeding gums and loosening of teeth.
- Vitamin A:
- This vitamin is important for maintaining mucous membranes in the mouth. It helps with the healing process and with the maintenance of salivary flow.
- A deficiency can lead to dry mouth, decreased salivary flow (which increases the risk of tooth decay and gum disease), and delayed healing of oral tissues.
- Vitamin B complex (including B2 Riboflavin, B3 Niacin, B6, and B12):
- Deficiencies in these vitamins can cause a range of oral health problems, including burning mouth syndrome, angular cheilitis (cracks at the corners of the mouth), recurrent aphthous stomatitis (canker sores), and atrophic glossitis (a smooth, red tongue).
- Vitamin B12 deficiency, in particular, can lead to glossitis, oral ulcers, and a feeling of burning in the mouth, which might mimic the symptoms of fungal infections.
- Calcium:
- While not a vitamin, calcium is an essential mineral for oral health, crucial for the development and maintenance of strong teeth and bones.
- A calcium deficiency can lead to dental changes, such as tooth decay and periodontal disease, due to diminished bone density and the weakening of the jawbone that supports the teeth.
FAQ on Mandibular Tori Vitamin Deficiency
What causes mandibular tori to grow?
Mandibular tori are thought to grow due to a combination of genetic factors and local stressors on the jaw, such as teeth grinding (bruxism) and jaw clenching. While the exact cause is not completely understood, these factors are believed to contribute to their development.
How do I get rid of Tori naturally?
There is no natural method to completely get rid of mandibular tori once they have formed. Generally, they are harmless and only removed surgically if they cause discomfort, interfere with denture fitting, or lead to recurrent ulceration. Read more: Mandibular Tori Removal.
How do I stop my Tori from growing?
To prevent further growth of mandibular tori, addressing underlying behaviors such as teeth grinding can be helpful. Using mouth guards or undergoing stress-relief therapies may reduce the mechanical stress on the jaw that contributes to tori growth.
What ethnicity has mandibular tori?
Mandibular tori are more commonly observed in certain ethnic groups, particularly in Asians and Inuits, suggesting a genetic predisposition. However, they can occur in any ethnic group. The prevalence can vary widely, with some studies showing higher rates in these populations.
Sources:
Fact Checked
Our dedicated team rigorously evaluates every article and guide to ensure the information is factual, up-to-date, and free of bias.
Updated Regularly
We update our articles and reviews regularly to ensure you have access to the latest data in the dental industry.
The content on Dental3DU’s blog is intended for educational purposes only. This information should not be relied upon as professional medical counsel. Be sure to always consult with your dentist about the dangers and benefits of any medication, treatment or procedure.